Understanding CNC Machines-A Comprehensive Overview of CNC Machining
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines stand as pivotal tools that have revolutionized the production process across various industries. From automotive to aerospace, and from electronics to healthcare, CNC machines play a crucial role in shaping precision parts and components with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency.
Introduction to CNC Machines
CNC machines are automated tools controlled by computer programs. They operate on predefined instructions, known as G-code, which dictates the movements of the machinery. This automation allows for precise and repetitive tasks that are essential in manufacturing complex geometries and intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve manually.
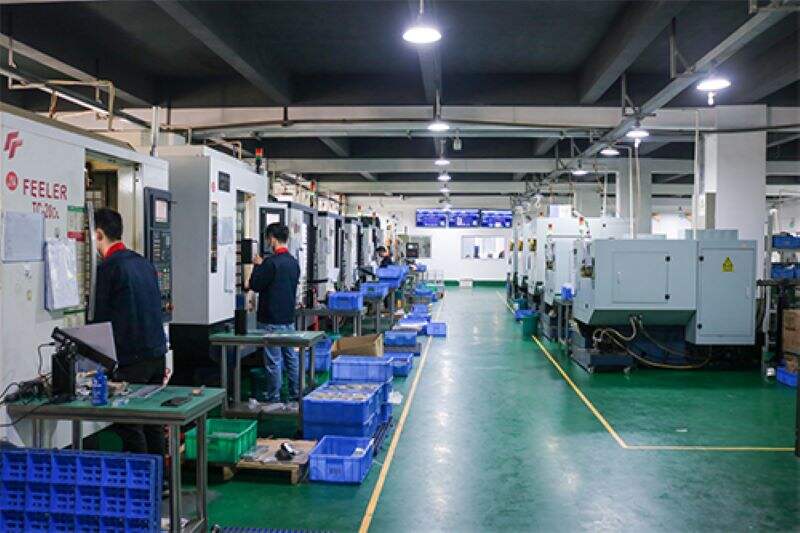

Key Components and Types of CNC Machines
The core components of a CNC machine typically include the control unit, which interprets the G-code instructions, the drive system that moves the machine axes, and the tooling or workholding devices that secure the material being worked on. CNC machines come in various types tailored to specific tasks:
1.CNC Mills: These machines use rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece. They are versatile and can produce a wide range of shapes, slots, holes, and threads.
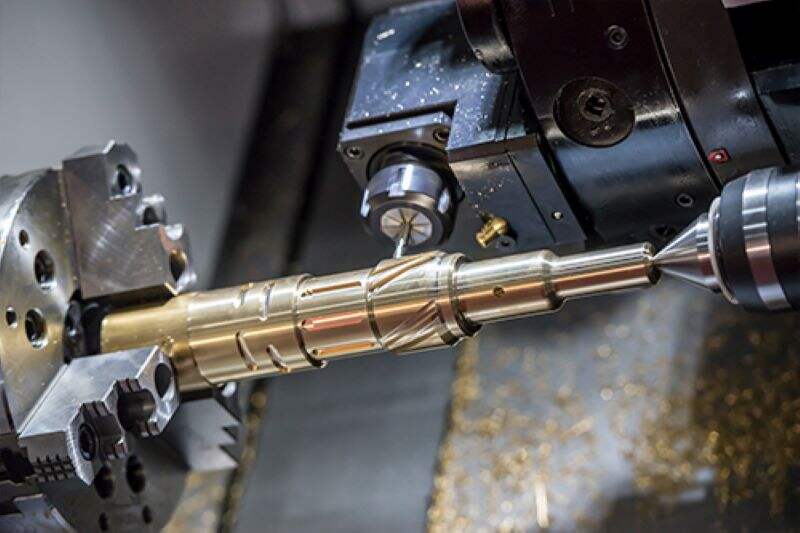

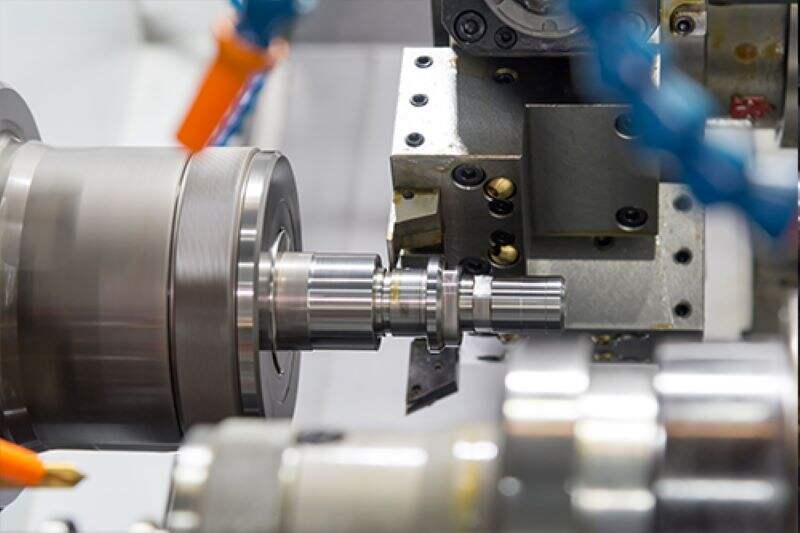
2.CNC Lathes: Lathes rotate the workpiece on its axis while cutting tools move along it to shape the material. They are ideal for cylindrical parts and turning operations.
3. CNC Routers: Used primarily for cutting and shaping wood, plastics, and composites, routers are equipped with a spindle that holds cutting tools.
4.CNC Plasma Cutters and Waterjets: These machines use plasma or waterjet technology, respectively, to cut through materials such as metal, stone, or glass with high precision.
Advantages of CNC Machining
The advantages of CNC machining are manifold:
1. Precision: CNC machines can achieve extremely tight tolerances, ensuring consistent quality across production batches.
2. Efficiency: Automation reduces human error and increases productivity by running continuously, often 24/7.
3.Flexibility: With the ability to change tooling and reprogram instructions swiftly, CNC machines can adapt to different manufacturing needs without extensive downtime.
Applications Across Industries
CNC machining finds applications in diverse sectors:
1.Automotive: Used for manufacturing engine components, chassis parts, and intricate assemblies.
2. Aerospace: Critical for producing aircraft components that demand high precision and reliability.
3. Medical: From surgical instruments to prosthetics, CNC machines craft complex medical devices with exacting specifications.

Future Trends and Innovations
Looking forward, advancements in CNC technology continue to push boundaries:
1. Additive Manufacturing: Integrating CNC with 3D printing for hybrid manufacturing processes.
2. IoT Integration: Smart CNC machines equipped with sensors for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
3.AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing automation and optimizing machining processes for greater efficiency and accuracy.
CNC machines epitomize the marriage of precision engineering and digital technology, reshaping the landscape of modern manufacturing. As industries evolve and demand for customization grows, CNC machining stands poised to play an even more pivotal role in shaping the future of production worldwide.


